To calculate result you have to disable your ad blocker first.
Decimal Point: Definition, Applications, and Examples

Publish Date: 13 Nov, 2023
Table of Content
In mathematics and numerical representations, the decimal point is critical. It's a punctuation mark that has the capability to modify the entire value of a number.
This composition will discuss the significance and operation of the decimal point. We'll discuss the decimal point in detail along with its applications and examples.
Decimal Point
In numerical representations, the decimal point is a punctuation mark that differentiates the whole number component from the fractional component. It is represented with a period or a dot. It displays a number change from an integral to a fractional component.
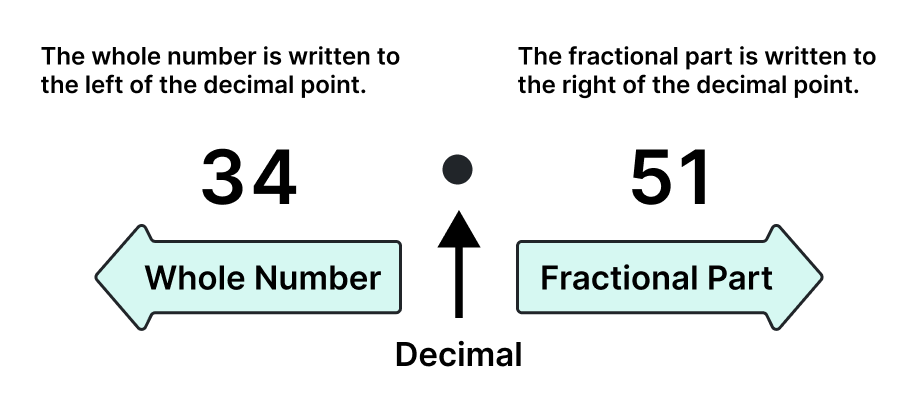
The above figure shows the number 34.51.
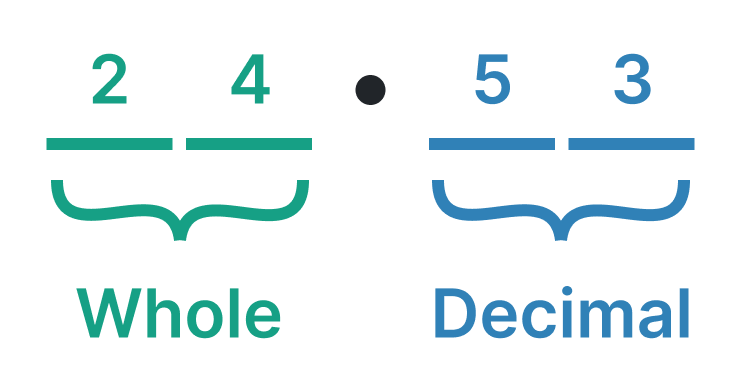
In the above figure, 24 represents the element of a whole number after a decimal point, the number 53 is known as the fractional element.
The fractional element is the number to the right of the decimal point whereas the whole element is the number to the left wing of the decimal point.
Because of the decimal point, we can snappily understand the decimal number.
- “And” is used as we read the decimal point.
We will try to understand it through the given figure.
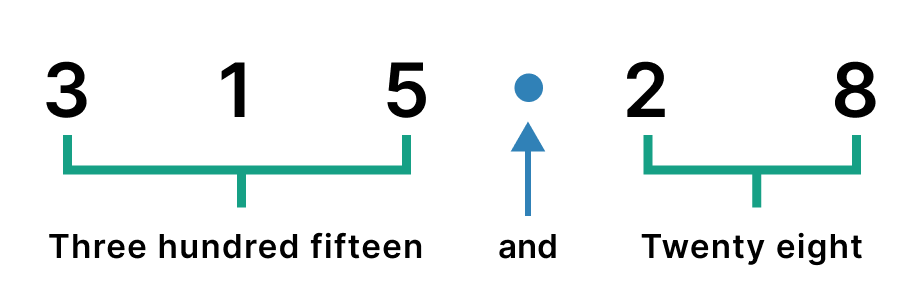
In the above figure, we have 315.28 which we can read as three hundred fifteen and twenty-eight.
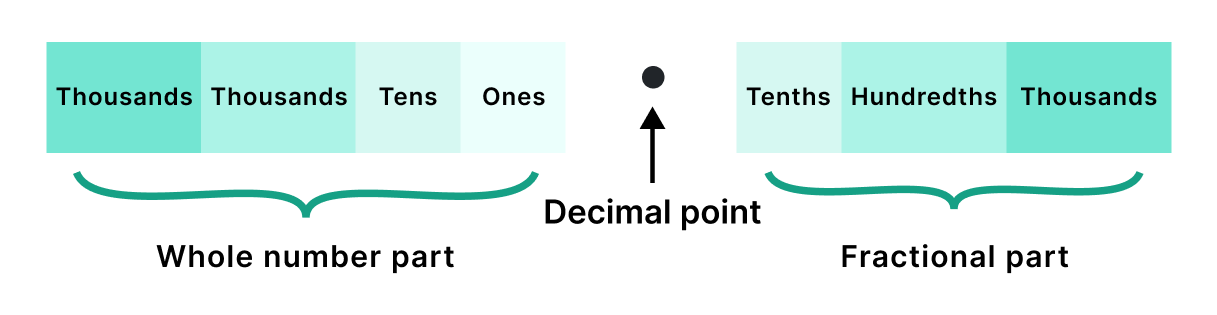
Place Value Chart of a Decimal:
The place value system was the same as the whole number, before the decimal point. But If we talk about the current time of decimal point, everything changes now.
Mathematical Operations with Decimal Points
- Addition and Subtraction
- Multiplication and Division
Addition and Subtraction: When adding or deducting decimal figures, the decimal points must be aligned for successful computation. The decimal point in the result will be in the same place as the decimal point in the figures being added or deducted.
Multiplication and Division: Multiplication and division with decimal numbers require careful consideration of the decimal point position. Multiplication and division of decimal numbers are fundamental mathematical operations involving multiplying or dividing numbers with decimal places.
In these operations, firstly we have to forget the decimal and simply we have to multiply or divide the number by using the traditional way of this operation, and at the end, we have to put the decimal point according to the given data.
Decimal point movement to the Left:
By dividing with 10 we can move one point of decimal from right to left.

= 543.26 ÷ 10
= 54326/100 * 1/10
= 54326/1000
= 54.326
Decimal point movement to the Right:
By multiplying with 10 we can move the one point of decimal from left to right.
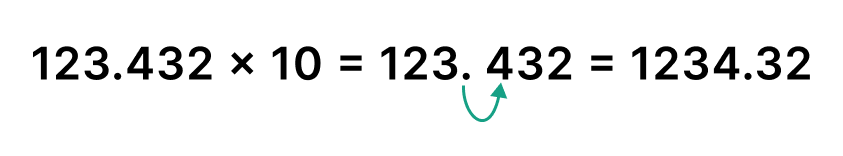
= 123.432 * 10
= 124.32
Applications of Decimal point:
- Financial Calculations
- Measurements and Conversions
- Scientific Notation
Financial Calculations:
Decimal points are essential in financial calculations, such as currency conversions, interest calculations, and tax computations. Precise handling of decimal points ensures accurate results, preventing errors that could have significant financial implications.
Measurements and Conversions:
Decimal points, such as length, weight, and volume, are commonly used in measurements. They allow for precise representation and conversions between different units of measurement.
E.g.,
The conversion from meters to centimeters involves shifting the decimal point two places to the right.
Scientific Notation:
Scientific notation is a compact way of representing very large or very small numbers. It uses decimal point notation and powers of 10 to express numbers in a concise and standardized format.
Challenges and Common Mistakes:
- Misplacement and Misinterpretation
- Decimal Point in Programming
Misplacement and Misinterpretation:
Misplacing or misinterpreting the decimal point can lead to substantial errors in calculations or measurements. Carelessness in placing the decimal point incorrectly can result in distorted values, inaccurate results, and potential misinterpretation of data.
Decimal Point in Programming:
In programming languages, handling decimal points requires attention to data types and formatting. Different programming languages may have specific rules and functions for working with decimal numbers. Incorrect usage of decimal points in programming can lead to bugs, computational errors, or unexpected behavior.
Examples
Some examples are as follows:
Example 1:
Add the given number which is in decimal form.
123.345, 245.123
Solution:
Step: Write the given data in the horizontal form and apply the operation of addition.
123.345
+245.123
368.468
Example 2:
Subtract the given number which is in decimal form.
345.456, 123.234
Solution:
Step: Write the given data in the horizontal form and apply the operation of Subtraction.
345.456
- 123.234
222.222

