To calculate result you have to disable your ad blocker first.
Digital Root: Definition, Applications and Calculations
Publish Date: 13 Nov, 2023
Table of Content
The digital root is also known as the additive digital root or the repeated digital sum. It is an enthralling and important mathematical idea. It is a method of collecting the digits of a number until a single-digit result is obtained. The repeated summing method can show astonishing patterns and numerical properties.
In this article, we will explore the definition, applications, and calculations of digital roots.
What is a Digital Root?
The repeated digital sum, also known as the digital root, is the single-digit number produced by recursively adding the digits of a given integer until only one remains. This action is repeated again and again until we cannot get a single digit which is known as digital root.
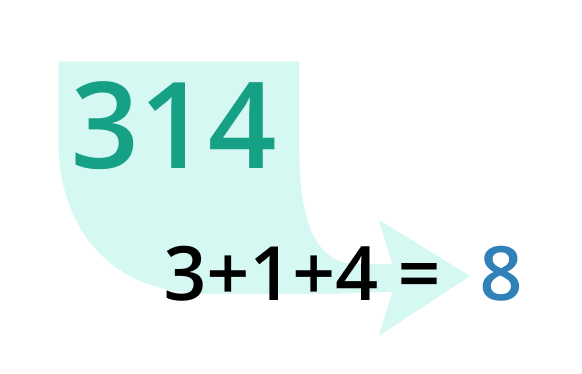
For instance, the digital root of 365 would be calculated as follows: 3 + 6 + 5 = 14, and 1 + 4 = 5. Hence, the digital root is 5.
Digital root holds a significant role in various mathematical and number theory concepts. Also, digital roots can help identify patterns and recurring cycles in numbers, providing mathematicians and researchers with valuable insights into the behavior of numbers.
How to Calculate the Digital Root?
Follow the below process to calculate a digital root.
- Start by adding up the individual digits of the number. If the resulting sum is a single digit then the resulting digit is the digital root.
- If the sum of any number contains more than one number. Then, we have to sum up the resulting number and we will continue this process till we don’t get a single digit.
Let’s try to understand it with the help of an example having a number of 587.
By adding the digits, we get 5 + 8 + 7 = 20. As we can see the 20 is not a single digit. So, we have to repeat the process by adding 2 + 0 = 2. So, the digital root is 2 as it is a single digit.
Examples
Some examples of finding a digital root are as follows:
Example 1:
Determine the digital root of 43.
Solution:
Step 1: Sum up the digits
= 4 + 3
Step 2: Resulting digital root value
= 7
So, the resulting digital value is 7 which we get after applying the addition operation to it.
Example 2:
Evaluate the digital root of 3625.
Solution:
Step 1: Add all the digits
= 3 + 6 + 2 + 5
= 16
Step 2: Repeat the operation of summing up
= 1 + 6
= 7
So, the resulting digital root of 3625 is 7.
Example 3:
After adding the numbers 413 and 321 calculate the digital root of the resulting number and compare it with the digital root of individual 413 and 321.
Solution:
Step 1: Add the given number
4 1 3
+ 3 2 1
7 3 4
Step 2: Sum up the resulting value
= 7 + 3 + 4
= 14
Step 3: Repeat the same process for the 14
= 1 + 4
= 5
So, the digital root after adding 413 and 321 is 5. Now, we have to compare it with the digital root of individual numbers 413 and 321.
Step 4: Sum up the 413
= 4 + 1 + 3
= 8
Step 5: Sum up the 321
= 3 + 2 + 1
= 6
Step 6: Add the digital root which we got individually
= 8 + 6
= 14
Step 7: Sum up the 14
= 1 + 4
= 5
So, if compare the sum of 413 and 321 we get the same answer as we got individually and the answer is 5 in both cases.
Try to understand it with the help of a figure.
Application of Digital Root in Number Theory:
Some applications of digital root in number theory are as follows:
- Congruence
- Periodicity
- Number Classification
- Prime Numbers
- Recursive Sequences
- Number Transformation:
Congruence:
The digital root can be used to study the congruence properties of numbers.
Periodicity:
The digital root exhibits periodicity in its values. It repeats every nine consecutive integers.
Number Classification:
The digital root can be employed to classify numbers into different categories.
Prime Numbers:
The digital root has connections to prime numbers.
Recursive Sequences:
The digital root can be used in generating and analyzing recursive sequences.
Number Transformations:
The digital root can be part of various number transformations and operations.

