To calculate result you have to disable your ad blocker first.
Shell Method Calculator
To find the volume, Enter the function, select the variable, enter the limit values, and click calculate button using shell method calculator
Shell Method Calculator
Shells method calculator is used to find the volume and surface area of the given function. This shell calculator solves the definite integral of the function by applying the upper and lower limit values of the function.
It provides the solution with steps of the given function.
What is the shell method?
In mathematics, the shell method is a technique of determining volumes by decomposing a solid of revolution into cylindrical shells. It is the alternate way of the wisher method. The volume of the cylinder is usually equal to the πr2h.
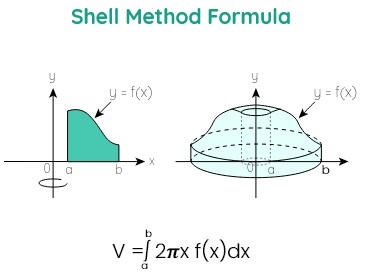
Formulas of shell method
There are different kinds of formulas for the shell method depending on the axis of curves.
About y-axis
Revolving the area under the curve of f(x).
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _a^b\:\)x f(x) dx
About x-axis
Revolving the area under the curve of f(y).
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _a^b\:\)y f(y) dy
Between two curves about the y-axis
Revolving the area between two curves f(x) and g(x)
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _a^b\:\)x[f(x) – g(x)] dx
Between two curves about the x-axis
Revolving the area between two curves f(y) and g(y)
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _a^b\:\)y[f(y) – g(y)] dy
Between two curves about x = h
Revolving the area between two curves f(x) and g(x)
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _a^b\:\)(x – h) [f(x) – g(x)] dx
Between two curves about y = k
Revolving the area between two curves f(y) and g(y)
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _a^b\:\)(y – k) [f(y) – g(y)] dy
The above six formulas are used to solve the problems of the shell method in different scenarios.
How to calculate the shell method?
Below are a few solved examples of the shell method.
Example 1:
Calculate the shell method about the y-axis if f(x) = 6x2 + 4 and the interval is {2, 3}.
Solution
Step 1: Take the given information.
f(x) = 6x2 + 4
Lower limit = a = 2
Upper limit = b = 3
Step 2: Take the formula of the shell method about the y-axis.
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _a^b\:\)x f(x) dx
Step 3: Substitute the given value in the formula.
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _2^3\:\)x [6x2 + 4] dx
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _2^3\:\)[6x3 + 4x] dx
Step 4: Calculate the integral of the above expression.
= 2π [\(\int _2^3\:\)[6x3] dx + \(\int _2^3\:\)[4x] dx]
= 2π [[6x3+1/ 3 + 1]32 + [4x1+1/1 + 1]32]
= 2π [[6x4/4]32+ [4x2/2]32]
= 2π [3/2[x4]32 + 2[x2]32]
Apply limits by using the fundamental theorem of calculus.
= 2π [3/2[34 – 24] + 2[32 – 22]]
= 2π [3/2[81 – 16] + 2[9 – 4]]
= 2π [3/2[65] + 2[5]]
= 2π [195/2 + 10]
= 2π [97.5 + 10]
= 2π [107.5]
= 215π
Step 5: Now substitute the value of π = 3.14
Volume = V = 215 π
Volume = V = 215(3.14)
Volume = V = 675.1
Example 2:
Calculate the shell method about the x-axis if f(y) = 2y + 6 and the interval is {2, 3}.
Solution
Step 1: Take the given information.
f(y) = 2y + 6
Lower limit = a = 2
Upper limit = b = 3
Step 2: Take the formula of the shell method about the x-axis.
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _a^b\:\)y f(y) dy
Step 3: Substitute the given value in the formula.
Volume = V = 2π \(\int _2^3\:\)y [2y + 6] dy
Volume = V = 2π\(\int _2^3\:\)[2y2 + 6y] dy
Step 4: Calculate the integral of the above expression.
= 2π [ \(\int _2^3\:\)[2y2] dy +\(\int _2^3\:\)[6y] dy]
= 2π [[2y2+1/ 2 + 1]32 + [6y1+1/1 + 1]32]
= 2π [[2y3/3]32 + [6y2/2]32]
= 2π [2/3[y3]32 + 3[y2]32]
Apply limits by using the fundamental theorem of calculus.
= 2π [2/3[33 – 23] + 3[32 – 22]]
= 2π [2/3[27 – 8] + 3[9 – 4]]
= 2π [2/3[19] + 3[5]]
= 2π [38/3 + 15]
= 2π [12.67 + 15]
= 2π [27.67]
= 55.34π
Step 5: Now substitute the value of π = 3.14
Volume = V = 55.34 π
Volume = V = 55.34(3.14)
Volume = V = 173.7676
Reference
- What is the Shell method? Brilliant Math & Science Wiki.
- Formulas of shell method. The Story of Mathematics -

